
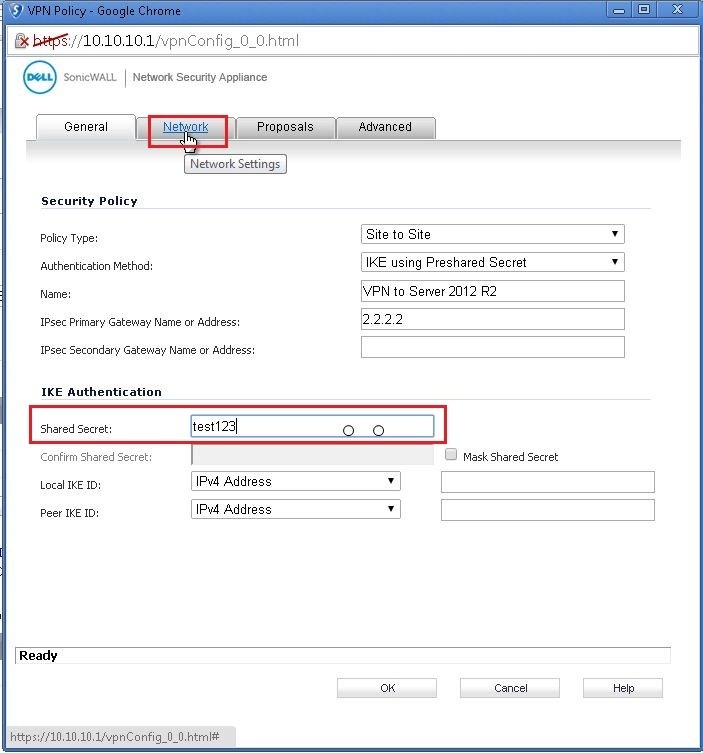
On Linux, you can use the command line to connect to your VPN server. When you are done, click OK to save your changes and continue to the next step. You will need to provide a name for your VPN server (ex: server1) and a secret key (generated randomly during setup) to connect to it. From the menu, choose Preferences, then click the + button to add a new VPN server. On macOS, you can use the OpenVPN GUI tool to connect to your server and begin setting up your VPN. Once you download and install the Open VPN client, you can connect to your server. You can download and install the Open VPN client from the OpenVPN website. The VPN software maintains active communication with a server providing you with a secure connection to a remote network (typically during setup, your device will automatically connect to a server offering you a secure connection to a remote network). OpenVPN is a free and open source VPN solution available for macOS, Linux, and Windows. Next, you will need to download and install the Open VPN software on your device.
Ip addr add 192.168.1.1/24 dev eth0 Step 2: Install the VPN Client On Linux, type the following command to generate a private network with the IP address 192.168.1.1: Once you click OK, the network will be created and you can proceed to Step 2. A window will pop up where you can enter a name for your new network and choose the type of security you wish to use (IPv4 or IPv6) and whether you’d like the network to be private (yes) or public (no). To create a network on macOS, open Network Preferences and click the + button to add a new network interface. Once you are assigned an IP address, you can create a network with any name you choose. Because IP addresses are assigned to devices dynamically by your Internet service provider (ISP), you will need to register your device with the ISP so it can be assigned an IP address. Devices on your network communicate using IP addresses, which are numerical labels assigned to devices on a network that ensure all communications are unambiguous. A network is a collection of devices (such as computers, smartphones, and tablets) that can communicate with one another. The first step in setting up a VPN is to create a secured network using the IP protocol. This article will guide you through the steps necessary to connect to a VPN using the Open VPN plug-in for the open source web server, Nginx. VPNs can be configured to work with all major broadband providers and are compatible with all major operating systems including macOS, Linux, and Windows. Having a VPN allows you to control who has access to what on your network and potentially increase your security by encrypting all traffic, including browsing history, that passes through your network. A Virtual Private Network (VPN) provides a confidential and secure connection between two or more remote locations over public networks such as the Internet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
